前言
Paxos算法应该算是分布式系统中最赫赫有名的算法了,就如同江湖上那句 “为人不识陈近南,纵称英雄也枉然”,Paxos在分布式中的地位,只会比陈近南在江湖上的地位更高。
按照我的打算,这个PAXOS系列,应该有3篇文章,我并不打算一上来就介绍Paxos的原理,因为势必太枯燥,我们小时候学习数学也是从1+1开始,然后倒引申到变量,介绍一元一次方程 二元一次方程,最后引申到行列式 矩阵 线性代数。从逻辑上讲,为什么不直接学习线性代数呢? 不直观,而且不符合人类认知事物的规律。
首先要介绍下,为什么ceph-mon需要这个Paxos算法。举个简单的例子,如果两个client都需要写入同一个cephfs上的文件,那么它们需要OSDMap,因为必须要根据OSDMap和文件名来决定要写到哪些OSD上,注意client A和Client B看到的OSDMap必须是一致的,否则的话会造成不一致。
因此我们看出来了,对于分布式存储来讲,一致性( consensus )是一个强需求。而对于分布式consensus来讲,几乎就等同于Paxos。
世界上只有一种一致性协议,就是Paxos
其他协议要么是paxos的简化,要么是错误的
本文是第一篇,用来介绍正常的一次Proposal应该是怎么样的。
Paxos 规则
角色
- Proposer 提案者,它可以提出议案
- Proposal 未被批准的决议称为提案,由Proposer提出,一个提案由一个编号和value形成的对组成,编号非常重要,保证提案的可区分性。
- Acceptor 提案的受理者,可以简单理解为独立法官,有权决定接受收到的提案还是拒绝提案。当然接受还是拒绝是有一定的规则的。
- Choose 提案被批准,被选定。当有半数以上Acceptor接受该提案时,就认为该提案被选定了
- Learner 旁观者,需要知道被选定的提案的那些人。Learner只能获取到被批准的提案。
算法
这里并不打算推导Paxos算法,或者证明算法的正确性,只介绍怎么做:
-
P1: 一个acceptor必须通过(accept)它收到的第一个提案。
P1a:当且仅当acceptor没有回应过编号大于n的prepare请求时,acceptor接受(accept)编号为n的提案。 -
P2: 如果具有value值v的提案被选定(chosen)了,那么所有比它编号更高的被选定的提案的value值也必须是v。
P2c:如果一个编号为n的提案具有value v,那么存在一个多数派,要么他们中所有人都没有接受(accept)编号小于n
的任何提案,要么他们已经接受(accept)的所有编号小于n的提案中编号最大的那个提案具有value v。
ceph中的 Paxos 实现
截止到本文,只会以正常流程为主,并不会介绍异常恢复过程,那是下一篇的主题。我们学习下面内容的时候,要注意两点
- 代码如何实现的Paxos的算法,和上一节的内容对应
- 正常情况下的代码,做了那些准备工作,看似无用,其实用于异常发生时的恢复
何时需要发起提案Proposal
Paxos的Trigger点总是要发起提案,那么ceph中需要发起提案的地方,大抵有以下三种:
-
ConfigKeyService在修改或删除key/value对的时候。
ceph提供了分布式的key-value服务,这个服务讲ceph-mon当成存储k/v的黑盒子。用户可以使用如下命令存放k/v
ceph config-key put key value ceph config-key get key ceph config-key del keyceph相关的函数接口在ConfigKeyService::store_put和store_delete
void ConfigKeyService::store_put(string key, bufferlist &bl, Context *cb) { bufferlist proposal_bl; MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef t = paxos->get_pending_transaction(); t->put(STORE_PREFIX, key, bl); if (cb) paxos->queue_pending_finisher(cb); paxos->trigger_propose(); } void ConfigKeyService::store_delete(string key, Context *cb) { bufferlist proposal_bl; MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef t = paxos->get_pending_transaction(); t->erase(STORE_PREFIX, key); if (cb) paxos->queue_pending_finisher(cb); paxos->trigger_propose(); } -
Paxos以及PaxosService对数据做trim的时候,trim的目的是为了节省存储空间,参见Paxos::trim和PaxosService::maybe_trim
注意,PaxosService是在Paxos基础上,封装了一些接口,用来构建基于Paxos的服务,早期的版本有六大PaxosService,如下图所示。
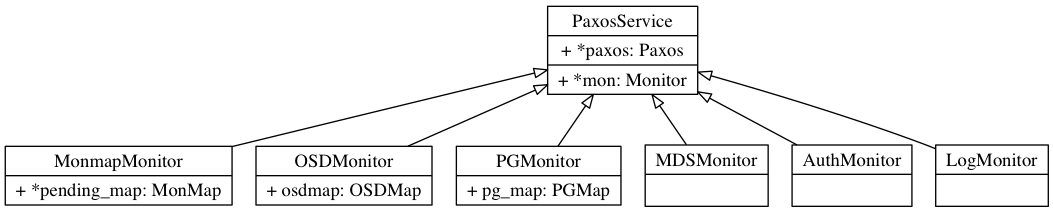
这些PaxosService,为了节省存储空间,也会通过调用maybe_trim来删除一些太老太旧的数据:
void Monitor::tick() { // ok go. dout(11) << "tick" << dendl; for (vector<PaxosService*>::iterator p = paxos_service.begin(); p != paxos_service.end(); ++p) { (*p)->tick(); (*p)->maybe_trim(); } ... }因此,每个Paxos都要定义自己的maybe_trim函数。
-
PaxosService的各种服务,需要更新值的时候,参见PaxosService::propose_pending
需要发起proposal的场合,主要是上面提到的这几种,在决定做proposal之前,都会讲操作封装成事务,存放在Paxos类的变量pending_proposal中.
/**
* Pending proposal transaction
*
* This is the transaction that is under construction and pending
* proposal. We will add operations to it until we decide it is
* time to start a paxos round.
*/
MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef pending_proposal;
/**
* Finishers for pending transaction
*
* These are waiting for updates in the pending proposal/transaction
* to be committed.
*/
list<Context*> pending_finishers;
/**
* Finishers for committing transaction
*
* When the pending_proposal is submitted, pending_finishers move to
* this list. When it commits, these finishers are notified.
*/
list<Context*> committing_finishers;
事务操作pending_proposal会被编码到bufferlist中,作为此次决议的值,会存放在paxos相关的k/v中,key为版本号, value为bufferlist二进制数据。commit的时候需要将bufferlist中的二进制数据还原成transaction,然后执行其中的操作, 即让决议的值反应在各个服务中,更新相关map。
也就是说,事务操作的内容会被编码成bufferlist,这个二进制数据流作为value,而key会版本号,作为paxos的提案。
注意,很多逻辑完成Paxos提案全过程之后,会有一些回调函数,这些回调会暂时放入pending_finishers列表。当Paxos的滚滚车轮一旦启动,会存放入committing_finishers列表。
bool Paxos::trigger_propose()
{
if (is_active()) {
dout(10) << __func__ << " active, proposing now" << dendl;
propose_pending();
return true;
} else {
dout(10) << __func__ << " not active, will propose later" << dendl;
return false;
}
}
void Paxos::propose_pending()
{
assert(is_active());
assert(pending_proposal);
cancel_events();
bufferlist bl;
pending_proposal->encode(bl);
dout(10) << __func__ << " " << (last_committed + 1)
<< " " << bl.length() << " bytes" << dendl;
dout(30) << __func__ << " transaction dump:\n";
JSONFormatter f(true);
pending_proposal->dump(&f);
f.flush(*_dout);
*_dout << dendl;
/*pengding_proposal 就可以reset了*/
pending_proposal.reset();
/*已经开始处理,因此,讲pending_finishers的内容存放入committing_finishers*/
committing_finishers.swap(pending_finishers);
/*注意,掉用begin之前,先将状态改成STATE_UPDATING*/
state = STATE_UPDATING;
begin(bl);
}
介绍了这些基本知识之后,可以看下Paxos决议的整体流程了。整个流程的起点是void Paxos::begin(bufferlist& v)。注意,这个函数只能由mon leader 发起,Peon不会掉用 begin函数,提出议案。
当然了,Paxos算法并未规定,只能有一个Proposer,但是ceph的实现通过只允许mon leader发起提案,简化了代码处理的流程。
Paxos 正常工作流程
整体的流程入下图所示:
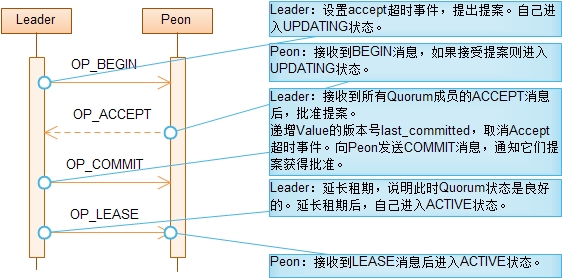
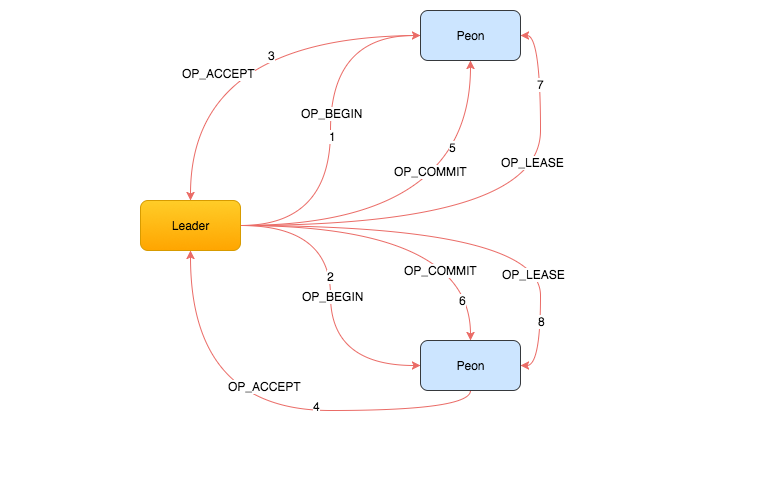
begin
void Paxos::begin(bufferlist& v)
{
dout(10) << "begin for " << last_committed+1 << " "
<< v.length() << " bytes"
<< dendl;
/*只有mon leader才能掉用begin,提出提案*/
assert(mon->is_leader());
assert(is_updating() || is_updating_previous());
// we must already have a majority for this to work.
assert(mon->get_quorum().size() == 1 ||
num_last > (unsigned)mon->monmap->size()/2);
// and no value, yet.
assert(new_value.length() == 0);
/*刚刚发起提案,目前还没有收到任何Acceptor的接受提案的信息*/
accepted.clear();
/*在接受提案的Acceptor中插入mon leader自己,因为自己的提案,自己不会拒绝*/
accepted.insert(mon->rank);
/*将 new_value 赋值为v,即将事务encode得到的bufferlist*/
new_value = v;
/*第一个commit,只有第一次提出提案的时候才会遇到*/
if (last_committed == 0) {
MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef t(new MonitorDBStore::Transaction);
// initial base case; set first_committed too
t->put(get_name(), "first_committed", 1);
decode_append_transaction(t, new_value);
bufferlist tx_bl;
t->encode(tx_bl);
new_value = tx_bl;
}
// store the proposed value in the store. IF it is accepted, we will then
// have to decode it into a transaction and apply it.
/*注意截下来的三个put操作是begin的一个关键地方,首先将事务encode过的bufferlist存放到*/
MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef t(new MonitorDBStore::Transaction);
t->put(get_name(), last_committed+1, new_value);
// note which pn this pending value is for.
t->put(get_name(), "pending_v", last_committed + 1);
t->put(get_name(), "pending_pn", accepted_pn);
dout(30) << __func__ << " transaction dump:\n";
JSONFormatter f(true);
t->dump(&f);
f.flush(*_dout);
MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef debug_tx(new MonitorDBStore::Transaction);
bufferlist::iterator new_value_it = new_value.begin();
debug_tx->decode(new_value_it);
debug_tx->dump(&f);
*_dout << "\nbl dump:\n";
f.flush(*_dout);
*_dout << dendl;
logger->inc(l_paxos_begin);
logger->inc(l_paxos_begin_keys, t->get_keys());
logger->inc(l_paxos_begin_bytes, t->get_bytes());
utime_t start = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
get_store()->apply_transaction(t);
utime_t end = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
logger->tinc(l_paxos_begin_latency, end - start);
assert(g_conf->paxos_kill_at != 3);
if (mon->get_quorum().size() == 1) {
// we're alone, take it easy
commit_start();
return;
}
// ask others to accept it too!
for (set<int>::const_iterator p = mon->get_quorum().begin();
p != mon->get_quorum().end();
++p) {
if (*p == mon->rank) continue;
dout(10) << " sending begin to mon." << *p << dendl;
MMonPaxos *begin = new MMonPaxos(mon->get_epoch(), MMonPaxos::OP_BEGIN,
ceph_clock_now(g_ceph_context));
begin->values[last_committed+1] = new_value;
begin->last_committed = last_committed;
begin->pn = accepted_pn;
mon->messenger->send_message(begin, mon->monmap->get_inst(*p));
}
/*注册超时*/
accept_timeout_event = new C_MonContext(mon, [this](int r) {
if (r == -ECANCELED)
return;
accept_timeout();
});
mon->timer.add_event_after(g_conf->mon_accept_timeout_factor *
g_conf->mon_lease,
accept_timeout_event);
}
注意,下面的代码是begin函数的关键:
MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef t(new MonitorDBStore::Transaction);
t->put(get_name(), last_committed+1, new_value);
// note which pn this pending value is for.
t->put(get_name(), "pending_v", last_committed + 1);
t->put(get_name(), "pending_pn", accepted_pn);
...
utime_t start = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
get_store()->apply_transaction(t);
utime_t end = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
logger->tinc(l_paxos_begin_latency, end - start);
首先,将要执行的transaction encode成的bufferlist先保存下来,并不真正执行,而仅仅是记录下,而这条信息以last_commit+1作为键值,一旦超过半数的Acceptor通过提案,那么就可以从leveldb或者rocksdb中根据last_commit+1,取出要执行的事务。
我们以如下值为例,介绍整个流程。
first_committed = 1
last_committed = 10
accepted_pn = 100
此次提案会新增如下信息到mon leader的 MonitorDBStore
# 此次提议增加的数据
v11=new_value; # 11是last_committed+1的值,这里key会有前缀,简单以v代替,new_value是最终事务的编码过的bufflerlist
pending_v=11
pending_pn=100
注意 get_store()->apply_transaction(t)执行之后,上述三个值就写入了mon leader的DB中了。
接下来的事情是向Peon发送OP_BEGIN消息,请Acceptor审核提案。
for (set<int>::const_iterator p = mon->get_quorum().begin();
p != mon->get_quorum().end();
++p) {
/*leader不必向自己发送*/
if (*p == mon->rank) continue;
dout(10) << " sending begin to mon." << *p << dendl;
MMonPaxos *begin = new MMonPaxos(mon->get_epoch(), MMonPaxos::OP_BEGIN,
ceph_clock_now(g_ceph_context));
/*将new_value和last_committed+1作为k/v对,发送个PEON*/
begin->values[last_committed+1] = new_value;
/*这两个值将来辅助Peon做决策,决定是否接受该提案*/
begin->last_committed = last_committed;
begin->pn = accepted_pn;
mon->messenger->send_message(begin, mon->monmap->get_inst(*p));
}
begin函数有特例,即整个集群只有一个mon,那么就可以跳过搜集其他Acceptor接受与否的过程,直接进入commit阶段:
/*只有自己存在,就没有必要征求意见了*/
if (mon->get_quorum().size() == 1) {
// we're alone, take it easy
commit_start();
return;
}
handle_begin
Peon收到OP_BEGIN消息之后,开始处理。
Peon只会处理pn>= accepted_pn的提案,否则就会拒绝该提案:
// can we accept this?
if (begin->pn < accepted_pn) {
dout(10) << " we accepted a higher pn " << accepted_pn << ", ignoring" << dendl;
op->mark_paxos_event("have higher pn, ignore");
return;
}
assert(begin->pn == accepted_pn);
assert(begin->last_committed == last_committed);
assert(g_conf->paxos_kill_at != 4);
logger->inc(l_paxos_begin);
/*将状态改成STATE_UPDATING*/
state = STATE_UPDATING;
lease_expire = utime_t(); // cancel lease
对于Peon来讲:
first_committed = 1
last_committed =10
accepted_pn = 100
v11=new_value
pending_v=11
pending_pn=100
当Peon决定接受提案的时候,将会讲new_value暂时保存到DB(leveldb or rocksdb)中,做的事情和mon leader是一致的:
// yes.
version_t v = last_committed+1;
dout(10) << "accepting value for " << v << " pn " << accepted_pn << dendl;
// store the accepted value onto our store. We will have to decode it and
// apply its transaction once we receive permission to commit.
MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef t(new MonitorDBStore::Transaction);
t->put(get_name(), v, begin->values[v]);
// note which pn this pending value is for.
t->put(get_name(), "pending_v", v);
t->put(get_name(), "pending_pn", accepted_pn);
....
logger->inc(l_paxos_begin_bytes, t->get_bytes());
utime_t start = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
get_store()->apply_transaction(t);
utime_t end = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
logger->tinc(l_paxos_begin_latency, end - start);
接下来,就可以讲接受提案的消息发送给mon leader,即发送OP_ACCEPT消息给mon leader。
// reply
MMonPaxos *accept = new MMonPaxos(mon->get_epoch(), MMonPaxos::OP_ACCEPT,
ceph_clock_now(g_ceph_context));
accept->pn = accepted_pn;
accept->last_committed = last_committed;
begin->get_connection()->send_message(accept);
handle_accept
mon leader自从向所有的peon发送了OP_BEGIN消息之后,就望穿秋水地等待回应。
// leader
void Paxos::handle_accept(MonOpRequestRef op)
{
op->mark_paxos_event("handle_accept");
MMonPaxos *accept = static_cast<MMonPaxos*>(op->get_req());
dout(10) << "handle_accept " << *accept << dendl;
int from = accept->get_source().num();
if (accept->pn != accepted_pn) {
// we accepted a higher pn, from some other leader
dout(10) << " we accepted a higher pn " << accepted_pn << ", ignoring" << dendl;
op->mark_paxos_event("have higher pn, ignore");
return;
}
if (last_committed > 0 &&
accept->last_committed < last_committed-1) {
dout(10) << " this is from an old round, ignoring" << dendl;
op->mark_paxos_event("old round, ignore");
return;
}
assert(accept->last_committed == last_committed || // not committed
accept->last_committed == last_committed-1); // committed
assert(is_updating() || is_updating_previous());
assert(accepted.count(from) == 0);
accepted.insert(from);
dout(10) << " now " << accepted << " have accepted" << dendl;
assert(g_conf->paxos_kill_at != 6);
// only commit (and expose committed state) when we get *all* quorum
// members to accept. otherwise, they may still be sharing the now
// stale state.
// FIXME: we can improve this with an additional lease revocation message
// that doesn't block for the persist.
if (accepted == mon->get_quorum()) {
// yay, commit!
dout(10) << " got majority, committing, done with update" << dendl;
op->mark_paxos_event("commit_start");
commit_start();
}
}
首先会做一些检查,比如accept->pn和accepted_pn是否相等之类的。如果通过检查,会讲对应peon放入accepted中,表示已经收到了来自该peon的消息,该peon已经同意该提案。
注意,和一般的Paxos不同的是,mon leader要收到所有的peon的OP_ACCEPT之后,才会进入下一阶段,而不是半数以上。
/*要收到所有的peon的OP_ACCEPT,才会进入到commit阶段*/
if (accepted == mon->get_quorum()) {
// yay, commit!
dout(10) << " got majority, committing, done with update" << dendl;
op->mark_paxos_event("commit_start");
commit_start();
}
leader在begin函数中,为了防止无法及时收集齐所有的OP_ACCEPT消息,注册了超时事件:
// set timeout event
accept_timeout_event = new C_MonContext(mon, [this](int r) {
if (r == -ECANCELED)
return;
accept_timeout();
});
mon->timer.add_event_after(g_conf->mon_accept_timeout_factor *
g_conf->mon_lease,
accept_timeout_event);
OPTION(mon_lease, OPT_FLOAT, 5) // lease interval
OPTION(mon_accept_timeout_factor, OPT_FLOAT, 2.0) // on leader, if paxos update isn't accepted
也就是说10秒中之内,不能收到所有的OP_ACCEPT,mon leader就会掉用accept_timeout函数,会掉用mon->bootstrap.
void Paxos::accept_timeout()
{
dout(1) << "accept timeout, calling fresh election" << dendl;
accept_timeout_event = 0;
assert(mon->is_leader());
assert(is_updating() || is_updating_previous() || is_writing() ||
is_writing_previous());
logger->inc(l_paxos_accept_timeout);
mon->bootstrap();
}
commit_start
当mon leader掉用commit_start的时候,表示走到了第二阶段。和二阶段提交有点类似,该提案已经得到了全部的peon的同意,因此可以大刀阔斧地将真正的事务提交,让提案生效。
void Paxos::commit_start()
{
dout(10) << __func__ << " " << (last_committed+1) << dendl;
assert(g_conf->paxos_kill_at != 7);
MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef t(new MonitorDBStore::Transaction);
// commit locally
/*last_committed的值 自加*/
t->put(get_name(), "last_committed", last_committed + 1);
// decode the value and apply its transaction to the store.
// this value can now be read from last_committed.
/*事务编码之后的bufferlist之前存储到了new_value这个成员,将事务decode,并追加到transaction中*/
decode_append_transaction(t, new_value);
dout(30) << __func__ << " transaction dump:\n";
JSONFormatter f(true);
t->dump(&f);
f.flush(*_dout);
*_dout << dendl;
logger->inc(l_paxos_commit);
logger->inc(l_paxos_commit_keys, t->get_keys());
logger->inc(l_paxos_commit_bytes, t->get_bytes());
commit_start_stamp = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
/*让事务生效,注意,此处是异步掉用*/
get_store()->queue_transaction(t, new C_Committed(this));
if (is_updating_previous())
state = STATE_WRITING_PREVIOUS;
else if (is_updating())
state = STATE_WRITING;
else
assert(0);
if (mon->get_quorum().size() > 1) {
// cancel timeout event
mon->timer.cancel_event(accept_timeout_event);
accept_timeout_event = 0;
}
}
此处事务的处理,是异步的,掉用了MonitorDBStore的queue_transaction函数。当事务完成之后,会掉用相关的回调函数。
void queue_transaction(MonitorDBStore::TransactionRef t,
Context *oncommit) {
io_work.queue(new C_DoTransaction(this, t, oncommit));
}
注意,当将事务放入队列之后,状态从UPDATING切换成了 STATE_WRITING。
回调函数定义在:
struct C_Committed : public Context {
Paxos *paxos;
explicit C_Committed(Paxos *p) : paxos(p) {}
void finish(int r) {
assert(r >= 0);
Mutex::Locker l(paxos->mon->lock);
paxos->commit_finish();
}
};
注意事务完成之后,会掉用commit_finish函数。
commit_finish函数
这个函数主要做三件事:
- 将内存中last_committed值+1
- 向peon发送commit消息
- 设置状态为refresh,刷新PaxosService服务
void Paxos::commit_finish()
{
dout(20) << __func__ << " " << (last_committed+1) << dendl;
utime_t end = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
logger->tinc(l_paxos_commit_latency, end - commit_start_stamp);
assert(g_conf->paxos_kill_at != 8);
// cancel lease - it was for the old value.
// (this would only happen if message layer lost the 'begin', but
// leader still got a majority and committed with out us.)
lease_expire = utime_t(); // cancel lease
/*last_committed可以自加了*/
last_committed++;
last_commit_time = ceph_clock_now(NULL);
// refresh first_committed; this txn may have trimmed.
first_committed = get_store()->get(get_name(), "first_committed");
_sanity_check_store();
/*给所有的peon发送OP_COMMIT消息*/
for (set<int>::const_iterator p = mon->get_quorum().begin();
p != mon->get_quorum().end();
++p) {
if (*p == mon->rank) continue;
dout(10) << " sending commit to mon." << *p << dendl;
MMonPaxos *commit = new MMonPaxos(mon->get_epoch(), MMonPaxos::OP_COMMIT,
ceph_clock_now(g_ceph_context));
commit->values[last_committed] = new_value;
commit->pn = accepted_pn;
commit->last_committed = last_committed;
mon->messenger->send_message(commit, mon->monmap->get_inst(*p));
}
assert(g_conf->paxos_kill_at != 9);
// get ready for a new round.
new_value.clear();
// WRITING -> REFRESH
// among other things, this lets do_refresh() -> mon->bootstrap() know
// it doesn't need to flush the store queue
assert(is_writing() || is_writing_previous());
state = STATE_REFRESH;
if (do_refresh()) {
commit_proposal();
if (mon->get_quorum().size() > 1) {
extend_lease();
}
finish_contexts(g_ceph_context, waiting_for_commit);
assert(g_conf->paxos_kill_at != 10);
finish_round();
}
}
需要注意的是,refresh完成后,在变回状态active之前,会开始lease协议,即发送lease消息给peon,这会帮助peon也变为active。
handle_commit
- 更新内存中和后端存储中last_committed值,即+1
- 将new_value中的值解码成事务,然后调用后端存储接口执行请求,这里采用同步写,和leader节点不一样
- 刷新PaxosService服务
void Paxos::handle_commit(MonOpRequestRef op)
{
op->mark_paxos_event("handle_commit");
MMonPaxos *commit = static_cast<MMonPaxos*>(op->get_req());
dout(10) << "handle_commit on " << commit->last_committed << dendl;
logger->inc(l_paxos_commit);
if (!mon->is_peon()) {
dout(10) << "not a peon, dropping" << dendl;
assert(0);
return;
}
op->mark_paxos_event("store_state");
/*store_state是函数之眼,同步地处理事务*/
store_state(commit);
if (do_refresh()) {
finish_contexts(g_ceph_context, waiting_for_commit);
}
}
handle_lease
peon收到延长租约的消息OP_LEASE之后,会掉用handle_lease,peon的状态从updating转变成active